CONTRACTS- MEANING AND IMPORTANCE | TYPES OF CONTRACTS – INDIAN CONTRACT ACT, 1872
INTRODUCTION
Contracts Drafting, A contract is described as an agreement between two or more parties that has a binding nature; in other words, an agreement that has legal enforceability. It establishes and defines the roles and responsibilities of all parties concerned. Because all commercial law transactions begin with an agreement or a contract, contracts are an important aspect of commercial law.
Business transactions involving the sale-purchase of goods or the exchange of services have become an important element of daily life. When parties enter into a business transaction, an agreement or contract is required to determine the parties’ rights, obligations, and responsibilities. In India, contracts are governed under the Indian Contract Act. An agreement which is enforceable by law is a contract, according to Section 2(h) of the Indian Contract Act, 1872 (referred to as the ICA). Contracts Drafting, In simple terms, an agreement is a pledge. Contracts Drafting- Every agreement isn’t a contract.
In order to qualify as a contract, agreements must meet specific conditions, such as consideration, parties must be competent, free consent between parties, legitimate object, and not expressly declared void by law. It is critical that the parties to a contract have the intention and mindset to enter into an agreement. “All contracts are agreements, but not all agreements are contracts. “First and foremost, one party makes an offer to another, which, if accepted by the person to whom it is made, results in a contract. Contracts Drafting, A contract is defined as an agreement that can be enforced in a court of law.
For more information, please contact us on info@trijuris.com or call us Mb. No. 85100 58386 or 9310 717274.
ESSENTIAL ELEMENTS OF CONTRACT
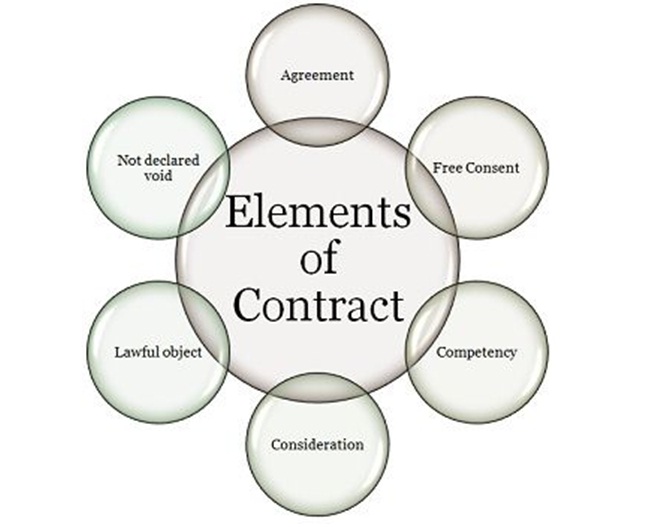
AGREEMENT:
An agreement, which is a result of offer and acceptance that generates consideration for the parties concerned, is the essential factor that makes a contract between parties. The initial step in the establishment of a contract is the offer or proposal. An Offer is when one individual expresses his or her desire to do or not do something to another. The offeror is the person one who makes the proposition or offer, while the offeree is the person to whom the offer is made. The offer must be made with the goal of forming a legal relationship. Acceptance refers to the offeree’s assent or consent to an offer. Acceptance can also be expressed by saying ‘yeah,’ ‘fine,’ or clicking on ‘I agree’ on a webpage. When the offer is accepted, it becomes a contract. A promise is another name for an agreement.
FREE CONSENT:
Another crucial feature of a contract is the parties’ consent, which indicates that the parties entering into the contract must agree on the same thing in the same sense. When the parties’ consent is not influenced by a force, undue influence, fraud, deception, or mistake, it is said to be free.
CAPACITY TO CONTRACT:
Competency refers to the parties’ ability to engage into a contract, i.e., they have reached the age of maturity, they must be of sound mind, and they are not barred from contracting under the law, such as alien enemies, foreign sovereigns, and so on.
CONSIDERATION:
The sum promised to be paid by the promise for the promisor’s commitment. It must be sufficient and legal. An offer to sell his car for ` 50,000 to B. B accepts the offer. In this case, the consideration of A is his car, and the consideration of B is 50.000.
LAWFUL OBJECT:
The object must be legal, or the deal will be ruled void.
NOT EXPRESSLY DECLARED VOID:
Contracts that are not specifically declared void, such as contracts in constraint of marriage, trade, or judicial procedures, should not be ruled void by the law.
OTHER KEY POINTS
- A contract must have at least 2 parties, one who proposes and the other who accepts the proposal.
- The parties must intend to create legal responsibility for one another when they sign the contract.
- It has to be written down.
- There must be a sense of clarity about what is being said. The parties’ words must be plain to them, i.e., neither party should interpret anything incorrectly, and there must be ad idem consensus.
- There should be a chance of completing the contract.
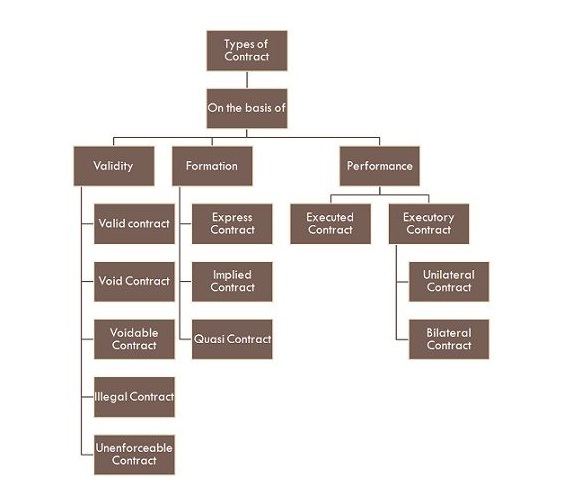
TYPES OF CONTRACTS
For more information, please contact us on info@trijuris.com or call us Mb. No. 85100 58386 or 9310 717274.
A- On the basis of validity:
- Valid Contract: A valid contract is one that is legally enforceable.
- Void Contract: A void contract is one that is no longer enforceable in a court of law.
- Voidable Contract: A voidable contract is one in which one of the contracting parties has the option of not completing his or her part. When a party’s permission is not freely given, the contract becomes voidable at the injured party’s discretion.
- Illegal Contract: An illegal contract is one that is prohibited by the law.
- Unenforceable Contract: An unenforceable contract is one that has a decent substance but is not enforceable owing to some difficulties.
B- On the basis of the formation
- Implied Contract: An implied contract is one that is formed by the implication of law or action.
- Express Contract: An express contract is one in which the terms of the contract are expressed either orally or in writing.
- Quasi-Contract: These are not actual contracts, but they are similar to contracts that are formed as a result of certain conditions.
C- On the basis of Performance
- Executed Contract: The term “executed contract” refers to a contract that has been completed.
- Executory Contract: An executory contract is one in which the contract’s obligation is to be fulfilled in the future. The executory contract is of two types – Unilateral Contract and Bilateral Contract.
IMPORTANCE-
- 1. They serve as a record of both parties’ obligations.
Contracts are, at their heart, relationships. First, two people agree to collaborate and form a bond that, if well-cultivated and mutually beneficial, can last for years. The visible expression of such a relationship is a contract. Contracts also bind both parties to the terms of their initial agreement.
In a SaaS contract, for example, one party promises to offer software to the other for a set period of time. The other party agrees to pay the provider the same amount of money for the same amount of time. A contract is, first and foremost, the trial that holds both parties accountable for the parameters they agreed to at the start of the relationship.
- 2. Agreements help to avoid disagreements and reduce risk.
Contracts are frequently subjected to a negotiating process to ensure that both parties get the best deal possible. Obviously, good negotiation should result in a mutually beneficial resolution that avoids future conflict and establishes the foundation for healthy collaboration. Contracts should have a full audit trail of every update, comment, and revision made if they are properly maintained. Surprisingly, many modern organizations have automated all of their operations except this one.
- 3. Contracts are used to collaborate and communicate.
Contracts are, by definition, relational and collaborative from the start. Through the construction of a contract, teams can work together to define their needs, fostering healthy communication and allowing cross-departmental collaboration. The collaboration continues once the contract is sent to a third party at the start of a business relationship. Finally, negotiating can be utilized to promote high-quality collaboration.
- 4. In a perfect world, agreements would also help generate revenue.
Contracts Drafting, Contracts are legally binding agreements in which 1 party agrees to provide services in exchange for money. Furthermore, being able to process contracts quickly and accurately helps businesses produce more income. A roadblock to a signed contract equals a roadblock to additional money. Faster contract processes, on the other hand, allow businesses to sign more transactions and earn more money.
- 5. They improve the efficiency of operations
Examining contracts procedure and determining the most pressing areas for change would aid firms in becoming more efficient as a whole. Working faster and wiser, on the other hand, necessitates the use of the appropriate tools. One of the greatest methods to automate contract operations is to use contract management software. Instead of tiresome emails, a few clicks will get you approval. Signatures are completed in days or hours rather than weeks or months. Clearly, having all people, processes, and documents in one place is critical for aligning with the current pace of business.
CONCLUSION
Contracts Drafting, A contract is nothing but a legally binding instrument between 2 parties that specifies and governs the rights as well as duties of the parties to an agreement, as can be seen from the above discussion. Because it complies with the law’s standards and approval, a contract is legally enforceable. Contracts Drafting, A contract usually entails the exchange of products, services, money, or the promise to exchange any of these. When a contract is breached, the law must provide the affected party with either legal remedies such as damages or cancellation. The Indian Contract Act, 1872 provides various provisions for the regulation of contracts entered into by competent parties. Contracts have great relevance in today’s world, as they are used to carry out and necessitate corporate activities.
For more information, please contact us on info@trijuris.com or call us Mb. No. 85100 58386 or 9310 717274.
